- +971-04-327-7068
- info@smasterdubai.com
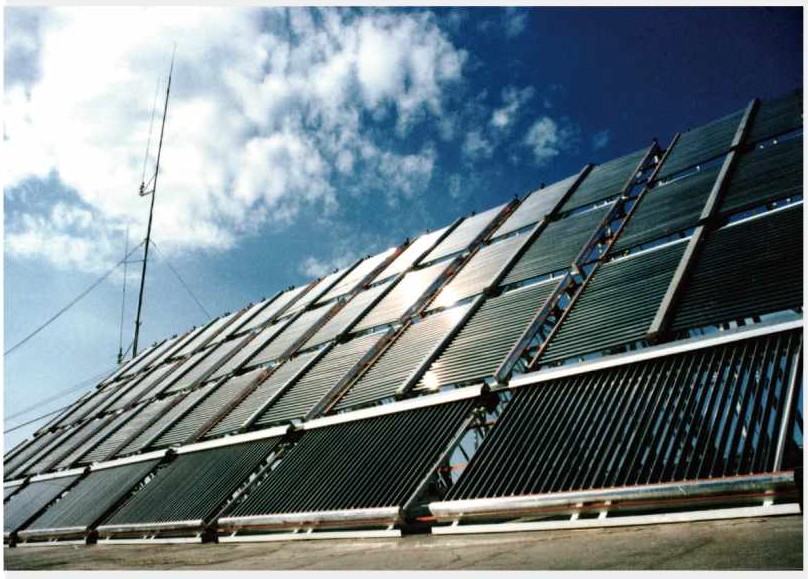


Manifold solar collectors are a type of solar thermal collector that are commonly used in solar water heating and space heating systems. These collectors are designed to efficiently absorb solar radiation and convert it into heat, which can then be used in a variety of applications.
Manifold solar collectors are typically made up of a series of parallel tubes or channels arranged in a manifold or header, and are often coated with a selective absorber material to enhance their efficiency. In this article, we will discuss the design, working principle, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of manifold solar collectors in greater detail.
Manifold solar collectors consist of a series of parallel tubes or channels arranged in a manifold or header. The tubes are usually made of copper, aluminum, or steel and are coated with a selective absorber material to enhance their solar radiation absorption efficiency. The manifold or header is typically made of the same material as the tubes and is responsible for distributing the fluid that is being heated.
The tubes are enclosed in an insulated casing or housing, which helps to minimize heat losses. The casing is usually made of metal or plastic and is designed to protect the tubes from damage and to prevent heat from escaping.
The selective absorber coating on the tubes is typically made of a black or dark-colored material that absorbs a high percentage of the solar radiation that strikes it. This allows the tubes to efficiently convert solar radiation into heat.
The insulation around the tubes and manifold is also an important component of the design. The insulation helps to minimize heat losses from the collector, which can be significant if the collector is not well insulated. The insulation can be made of a variety of materials, including foam, fiberglass, or mineral wool.
Overall, the design and construction of manifold solar collectors are relatively simple, which helps to keep costs low. However, the materials used must be carefully selected to ensure durability and long-term performance.
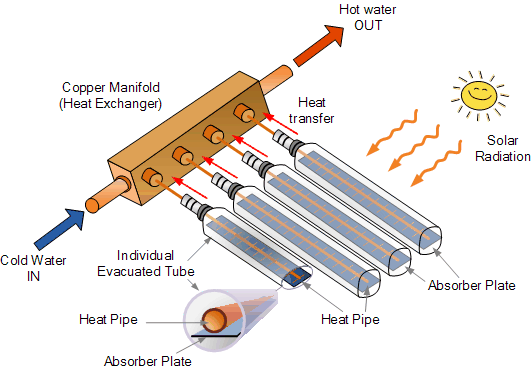
Manifold solar collectors work on the principle of solar thermal energy conversion. When solar radiation strikes the selective absorber coating on the tubes, it is absorbed and converted into heat. The heat is then transferred to a fluid that flows through the tubes.
The fluid used in manifold solar collectors is typically a mixture of water and an antifreeze solution, which is circulated through the collector by a pump. As the fluid flows through the tubes, it is heated by the solar radiation that is absorbed by the selective absorber coating.
Once the fluid has been heated, it is pumped out of the collector and transferred to a storage tank or directly to the heating system. In a solar water heating system, the heated fluid is typically used to preheat water that is then stored in a conventional water heater. In a space heating system, the heated fluid is typically used to directly heat the air or water that is circulated through the building.
The efficiency of manifold solar collectors depends on a variety of factors, including the design of the collector, the size and orientation of the collector, and the intensity and duration of the solar radiation. However, when properly designed and installed, manifold solar collectors can be highly efficient and can significantly reduce the amount of energy required to heat water or buildings.
There are two main types of manifold solar collectors: the single pipe (or tube) type and the double pipe (or tube) type.
In a single pipe manifold solar collector, each tube is connected to a separate header or manifold. This design allows the fluid to flow through each tube independently, which can help to improve the efficiency of the collector. However, it also requires more connections and fittings, which can increase the cost and complexity of the system.
In a double pipe manifold solar collector, each tube is connected to two headers or manifolds, creating a loop. The fluid flows through one tube and then returns through the other, creating a continuous circuit. This design is simpler and less expensive than the single pipe design, but it can be less efficient, especially if the flow rate is low.
Both single pipe and double pipe manifold solar collectors can be used in a variety of solar thermal applications, including solar water heating, space heating, and pool heating. The choice of collector will depend on a variety of factors, including the application, the available space, and the local climate.
Manifold solar collectors can be used in a variety of solar thermal applications, including:
Solar Water Heating: Manifold solar collectors are commonly used to heat water for domestic, commercial, and industrial applications. The heated water can be used for showering, washing, and other domestic purposes.
Space Heating: Manifold solar collectors can be used to heat buildings, both residential and commercial. The heated fluid can be used to directly heat the air or water that is circulated through the building.
Pool Heating: Manifold solar collectors are also commonly used to heat swimming pools. The heated water is circulated through a heat exchanger, which transfers the heat to the pool water.
Process Heating: Manifold solar collectors can be used to provide process heat for a variety of industrial applications, including food processing, textile manufacturing, and chemical production.
In all of these applications, manifold solar collectors can significantly reduce the amount of energy required to heat water or buildings, which can lead to significant cost savings and environmental benefits.
Advantages of Manifold Solar Collectors:
High Efficiency: Manifold solar collectors can have a higher efficiency compared to other types of solar collectors, especially if they are designed and installed properly.
Low Maintenance: Manifold solar collectors require very little maintenance, as they have no moving parts and are not subject to wear and tear.
Versatility: Manifold solar collectors can be used in a variety of solar thermal applications, making them a versatile and flexible option.
Long Lifespan: Manifold solar collectors can have a long lifespan, up to 25 years or more, with proper maintenance.
Environmentally Friendly: Manifold solar collectors produce no greenhouse gas emissions and help to reduce the dependence on fossil fuels.
Disadvantages of Manifold Solar Collectors:
Initial Cost: The initial cost of installing a manifold solar collector system can be relatively high compared to other types of heating systems.
Weather Dependent: The efficiency of manifold solar collectors is weather dependent and can be reduced on cloudy days or during winter months.
Space Requirements: Manifold solar collectors require a significant amount of space, which can be a limitation for some applications.
Complex Installation: The installation of manifold solar collectors can be complex and requires specialized knowledge and equipment.
Overall, despite the initial cost and installation complexities, manifold solar collectors offer many advantages over traditional heating systems, and they can provide significant cost savings and environmental benefits in the long run.
In conclusion, manifold solar collectors are an efficient and environmentally friendly option for heating water, buildings, and other applications that require heat. They have a long lifespan, low maintenance requirements, and can significantly reduce the amount of energy required for heating. However, they also have some limitations, such as the initial cost, weather dependence, and space requirements. Despite these limitations, manifold solar collectors offer many advantages over traditional heating systems and are a valuable addition to any sustainable energy system. With proper design, installation, and maintenance, manifold solar collectors can provide cost-effective and sustainable heating solutions for a variety of applications.
WhatsApp us