- +971-04-327-7068
- info@smasterdubai.com
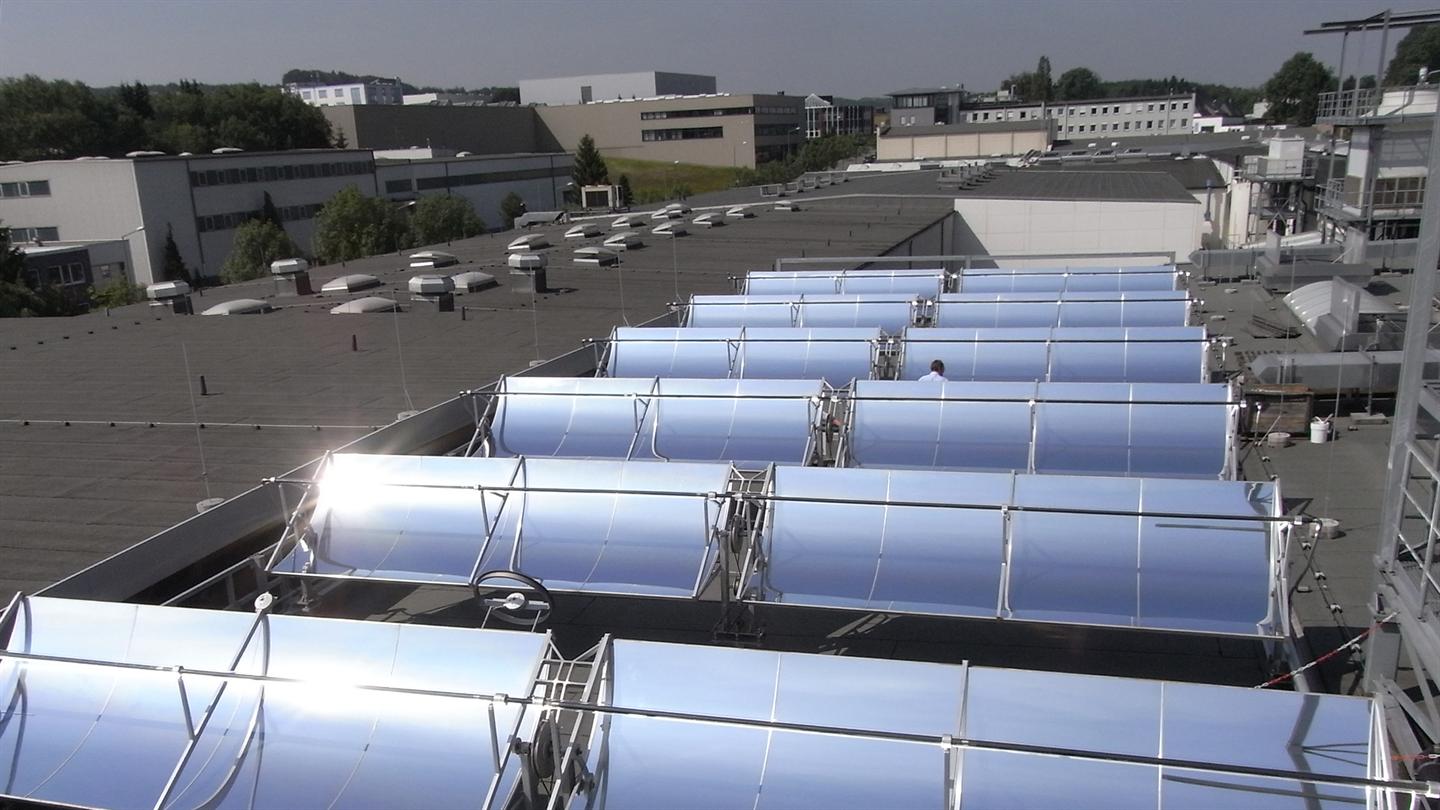

An introduction to industrial solar process heating systems involves providing an overview of this renewable energy technology and its applications in various industries. Industrial solar process heating systems utilize solar energy to heat water or other fluids for use in industrial processes.
They offer a reliable and cost-effective alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based heating systems and can help to reduce energy costs and carbon emissions in the industrial sector. In this article, we will explore how industrial solar process heating systems work, their components, applications, benefits, challenges, and considerations.
We will also examine case studies of successful implementations and discuss the potential for industrial solar process heating systems to contribute to a more sustainable and efficient industrial sector.
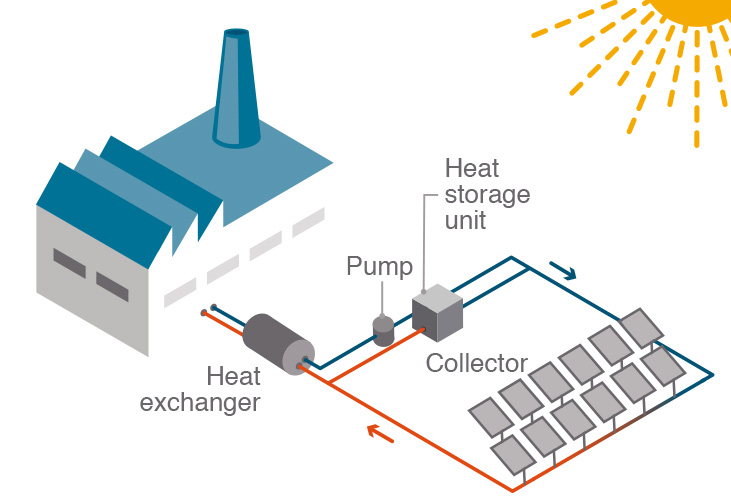
The components of an industrial solar process heating system can vary depending on the specific application and system design. However, the basic components of an industrial solar process heating system typically include:
Solar Collectors: The solar collectors are the heart of the system and are responsible for capturing and converting solar energy into heat. There are two main types of solar collectors used in industrial solar process heating systems: flat-plate and evacuated-tube collectors.
Heat Transfer Fluid: The heat transfer fluid circulates through the solar collectors and transfers the heat energy to a heat exchanger, which then heats water or other fluids for industrial processes. Common heat transfer fluids used in industrial solar process heating systems include water-glycol mixtures and thermal oils.
Heat Exchanger: The heat exchanger is responsible for transferring the heat from the heat transfer fluid to the water or other fluids used in industrial processes. There are different types of heat exchangers available, including plate and frame, shell and tube, and spiral heat exchangers.
Storage Tank: The storage tank is used to store the heated water or fluid until it is needed for industrial processes. The size of the storage tank depends on the specific application and system design.
Pumps and Controls: Pumps and controls are used to circulate the heat transfer fluid and control the system to ensure that it operates efficiently and effectively. The pumps also help to prevent the fluid from freezing in cold temperatures.
Backup Heating System: A backup heating system such as a gas or electric boiler may be included in the system to provide additional heat when solar energy is not sufficient to meet the required heating demand.
Insulation: Insulation is used to reduce heat losses from the storage tank and piping and to maintain the temperature of the heated water or fluid.
Proper sizing and selection of these components is essential to ensure that the industrial solar process heating system operates efficiently and effectively. System design and installation should be carried out by experienced professionals to ensure that the system is optimized for the specific application and location.
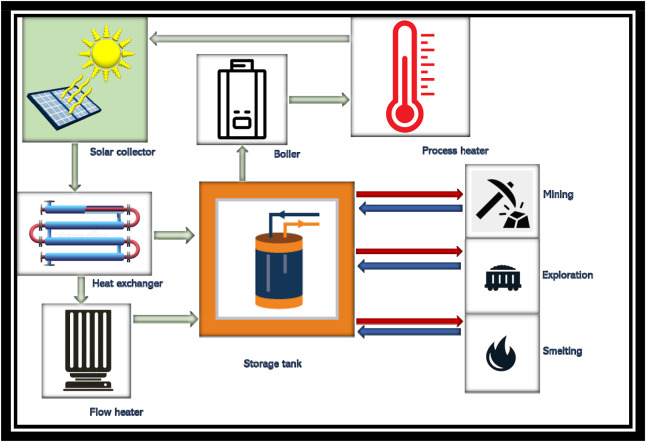
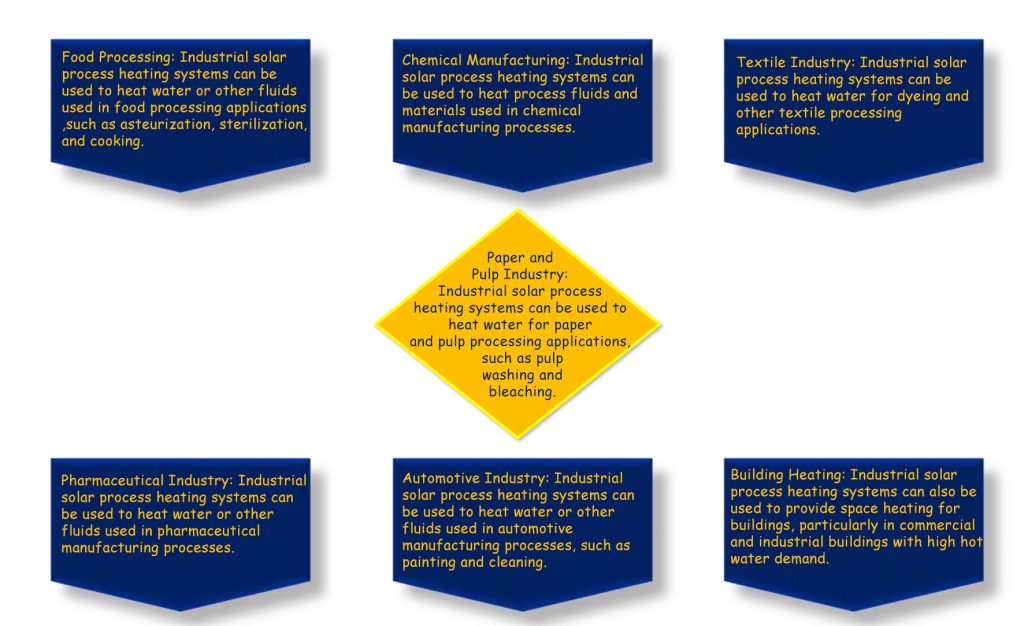
Industrial solar process heating systems can be used in a wide range of industrial applications where heat is required for production processes. Some of the common applications of industrial solar process heating systems include:
While industrial solar process heating systems offer many benefits, there are also some challenges and considerations that should be taken into account before implementing a solar process heating system. Some of these challenges and considerations include:
System Design: The design of the industrial solar process heating system should be carefully considered to ensure optimal efficiency and effectiveness. The size of the system, location of the collector, and type of storage tank are all important factors that should be taken into account.
System Maintenance: Industrial solar process heating systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Components such as pumps, valves, and collectors should be inspected and cleaned regularly to prevent malfunctions.
Weather Conditions: Solar process heating systems rely on sunlight to generate heat, which can be challenging during periods of cloudy weather. Backup heating systems should be in place to ensure consistent heat supply during periods of low solar radiation.
System Integration: The integration of the solar process heating system with existing industrial processes can be complex, and may require modifications to existing infrastructure.
Initial Investment: The initial investment required to install an industrial solar process heating system can be significant, and may require a long-term return on investment.
Regulatory Compliance: Industrial solar process heating systems may be subject to regulatory compliance requirements, such as building codes and safety standards, which should be carefully considered during the design and implementation phases.
Availability of Expertise: The installation and maintenance of industrial solar process heating systems may require specialized expertise, which may not be readily available in all areas.
In summary, while industrial solar process heating systems offer many benefits, there are also several challenges and considerations that should be taken into account before implementing a solar process heating system. These challenges and considerations should be carefully evaluated to ensure that the system is designed, implemented, and maintained effectively to maximize the benefits of the system.
There are several benefits of using industrial solar process heating systems, including:
Cost Savings: Industrial solar process heating systems can provide significant cost savings compared to conventional heating systems, as they utilize free solar energy to heat water or other fluids used in industrial processes.
Energy Independence: Industrial solar process heating systems can provide energy independence by reducing reliance on non-renewable energy sources, such as fossil fuels.
Environmental Sustainability: Industrial solar process heating systems are environmentally sustainable, as they produce zero greenhouse gas emissions and have a minimal impact on the environment.
Long-Term Reliability: Industrial solar process heating systems have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance, making them a reliable and cost-effective heating solution for industrial processes.
Government Incentives: Many governments offer incentives and tax credits for businesses that invest in renewable energy systems, including industrial solar process heating systems.
Improved Corporate Social Responsibility: The use of industrial solar process heating systems can improve a company’s corporate social responsibility profile by demonstrating a commitment to sustainable practices and reducing carbon footprint.
Increased Marketability: Companies that invest in industrial solar process heating systems can differentiate themselves from competitors by demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility, which can increase marketability and customer loyalty.
In summary, industrial solar process heating systems offer a range of benefits, including cost savings, energy independence, environmental sustainability, long-term reliability, government incentives, improved corporate social responsibility, and increased marketability.
Here are some examples of industrial solar process heating system case studies:
Solar Thermal Energy for Industrial Process Heat – Michigan, USA: In this case study, a solar thermal system was installed at a manufacturing facility to provide process heat for plating and anodizing operations. The system consisted of 16 solar collectors, a 1500-gallon storage tank, and a heat exchanger. The system provides over 50% of the facility’s annual process heat requirements, resulting in significant cost savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Solar Thermal for Industrial Process Heat – Ontario, Canada: In this case study, a solar thermal system was installed at a chemical manufacturing plant to provide process heat for chemical reactions. The system consisted of 260 solar thermal collectors, a 6,000-gallon storage tank, and a heat exchanger. The system provides over 25% of the facility’s annual process heat requirements, resulting in significant cost savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Solar Thermal Process Heat for Brewery – Australia: In this case study, a solar thermal system was installed at a brewery to provide process heat for brewing operations. The system consisted of 50 solar thermal collectors, a 5000-litre storage tank, and a heat exchanger. The system provides over 60% of the brewery’s annual process heat requirements, resulting in significant cost savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Solar Thermal for Industrial Drying Process – Maharashtra, India: In this case study, a solar thermal system was installed at a dairy plant to provide process heat for milk drying operations. The system consisted of 105 solar thermal collectors, a 60,000-litre storage tank, and a heat exchanger. The system provides over 50% of the facility’s annual process heat requirements, resulting in significant cost savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
These case studies demonstrate the effectiveness and cost savings of industrial solar process heating systems in a range of industries and applications.

In conclusion, industrial solar process heating systems offer a sustainable and cost-effective solution for meeting the process heating needs of various industries. By using solar energy to generate heat, these systems offer significant cost savings and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, designing, implementing, and maintaining these systems require careful consideration of several factors, including weather conditions, system integration, and regulatory compliance. Nevertheless, with careful planning and execution, industrial solar process heating systems can offer a reliable and sustainable source of process heat for industrial operations.
WhatsApp us